Assignment Problem: Meaning, Methods and Variations | Operations Research
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations.

Meaning of Assignment Problem:
An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total cost or maximize total profit of allocation.
The problem of assignment arises because available resources such as men, machines etc. have varying degrees of efficiency for performing different activities, therefore, cost, profit or loss of performing the different activities is different.
Thus, the problem is “How should the assignments be made so as to optimize the given objective”. Some of the problem where the assignment technique may be useful are assignment of workers to machines, salesman to different sales areas.
Definition of Assignment Problem:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Suppose there are n jobs to be performed and n persons are available for doing these jobs. Assume that each person can do each job at a term, though with varying degree of efficiency, let c ij be the cost if the i-th person is assigned to the j-th job. The problem is to find an assignment (which job should be assigned to which person one on-one basis) So that the total cost of performing all jobs is minimum, problem of this kind are known as assignment problem.
The assignment problem can be stated in the form of n x n cost matrix C real members as given in the following table:
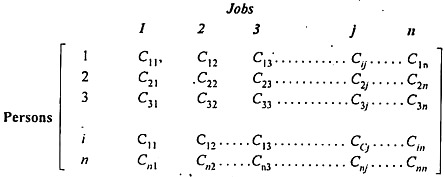

Operations Research - Definition and formulation of Assignment Problem | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
Chapter: 12th business maths and statistics : chapter 10 : operations research, definition and formulation of assignment problem.
Definition and formulation
Consider the problem of assigning n jobs to n machines (one job to one machine). Let C ij be the cost of assigning i th job to the j th machine and x ij represents the assignment of i th job to the j th machine.
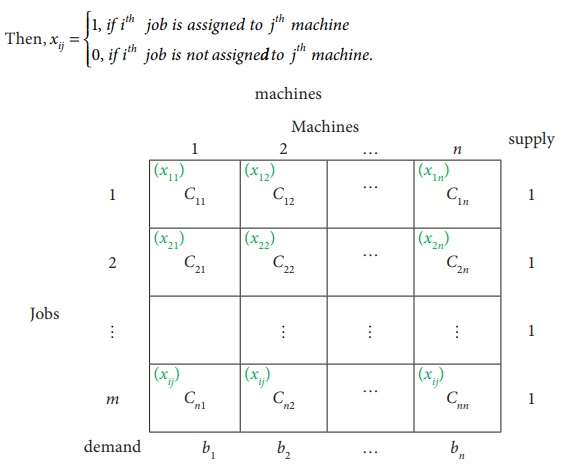
x ij is missing in any cell means that no assignment is made between the pair of job and machine.( i.e ) x ij = 0.
x ij presents in any cell means that an assignment is made their.In such cases x ij = 1
The assignment model can be written in LPP as follows
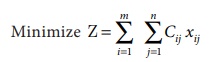
Subject to the constrains
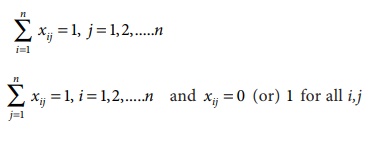
The optimum assignment schedule remains unaltered if we add or subtract a constant from all the elements of the row or column of the assignment cost matrix.
If for an assignment problem all C ij > 0 then an assignment schedule (x ij ) which satisfies ∑ C ij x ij = 0 must be optimal.
Related Topics
Privacy Policy , Terms and Conditions , DMCA Policy and Compliant
Copyright © 2018-2023 BrainKart.com; All Rights Reserved. Developed by Therithal info, Chennai.
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Science » Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research
Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research
Transportation and assignment models are special purpose algorithms of the linear programming. The simplex method of Linear Programming Problems(LPP) proves to be inefficient is certain situations like determining optimum assignment of jobs to persons, supply of materials from several supply points to several destinations and the like. More effective solution models have been evolved and these are called assignment and transportation models.
The transportation model is concerned with selecting the routes between supply and demand points in order to minimize costs of transportation subject to constraints of supply at any supply point and demand at any demand point. Assume a company has 4 manufacturing plants with different capacity levels, and 5 regional distribution centres. 4 x 5 = 20 routes are possible. Given the transportation costs per load of each of 20 routes between the manufacturing (supply) plants and the regional distribution (demand) centres, and supply and demand constraints, how many loads can be transported through different routes so as to minimize transportation costs? The answer to this question is obtained easily through the transportation algorithm.
Similarly, how are we to assign different jobs to different persons/machines, given cost of job completion for each pair of job machine/person? The objective is minimizing total cost. This is best solved through assignment algorithm.
Uses of Transportation and Assignment Models in Decision Making
The broad purposes of Transportation and Assignment models in LPP are just mentioned above. Now we have just enumerated the different situations where we can make use of these models.
Transportation model is used in the following:
- To decide the transportation of new materials from various centres to different manufacturing plants. In the case of multi-plant company this is highly useful.
- To decide the transportation of finished goods from different manufacturing plants to the different distribution centres. For a multi-plant-multi-market company this is useful.
- To decide the transportation of finished goods from different manufacturing plants to the different distribution centres. For a multi-plant-multi-market company this is useful. These two are the uses of transportation model. The objective is minimizing transportation cost.
Assignment model is used in the following:
- To decide the assignment of jobs to persons/machines, the assignment model is used.
- To decide the route a traveling executive has to adopt (dealing with the order inn which he/she has to visit different places).
- To decide the order in which different activities performed on one and the same facility be taken up.
In the case of transportation model, the supply quantity may be less or more than the demand. Similarly the assignment model, the number of jobs may be equal to, less or more than the number of machines/persons available. In all these cases the simplex method of LPP can be adopted, but transportation and assignment models are more effective, less time consuming and easier than the LPP.
Related posts:
- Operations Research approach of problem solving
- Introduction to Transportation Problem
- Procedure for finding an optimum solution for transportation problem
- Initial Basic Feasible Solution of a Transportation Problem
- Introduction to Decision Models
- Transportation Cost Elements
- Modes of Transportation in Logistics
- Factors Affecting Transportation in Logistics
One thought on “ Transportation and Assignment Models in Operations Research ”
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Techniques of Operations Research
The operations research expert has a wide array of methods and techniques available for solving problems.
Linear Programming . Linear Programming (LP) is a mathematical technique of assigning a fixed amount of resources to satisfy a number of demands in such a way that some objective is optimized and other defined conditions are also satisfied.
Transportation Problem . The transportation problem is a special type of linear programming problem, where the objective is to minimize the cost of distributing a product from a number of sources to a number of destinations.
Assignment Problem . Succinctly, when the problem involves the allocation of n different facilities to n different tasks, it is often termed as an assignment problem.
Queuing Theory . The queuing problem is identified by the presence of a group of customers who arrive randomly to receive some service. This theory helps in calculating the expected number of people in the queue, expected waiting time in the queue, expected idle time for the server, etc. Thus, this theory can be applied in such situations where decisions have to be taken to minimize the extent and duration of the queue with minimum investment cost.
Game Theory . It is used for decision making under conflicting situations where there are one or more opponents (i.e., players). In the game theory, we consider two or more persons with different objectives, each of whose actions influence the outcomes of the game. The game theory provides solutions to such games, assuming that each of the players wants to maximize his profits and minimize his losses.
Inventory Control Models . It is concerned with the acquisition, storage, handling of inventories so as to ensure the availability of inventory whenever needed and minimize wastage and losses. It help managers to decide reordering time, reordering level and optimal ordering quantity.
Goal Programming . It is a powerful tool to tackle multiple and incompatible goals of an enterprise.
Simulation . It is a technique that involves setting up a model of real situation and then performing experiments. Simulation is used where it is very risky, cumbersome, or time consuming to conduct real study or experiment to know more about a situation.
Nonlinear Programming . These methods may be used when either the objective function or some of the constraints are not linear in nature. Non-Linearity may be introduced by factors such as discount on price of purchase of large quantities.
"The best thing about future is that it comes one day at a time." - Abraham Lincoln
Integer Programming . These methods may be used when one or more of the variables can take only integral values. Examples are the number of trucks in a fleet, the number of generators in a power house, etc.
Dynamic Programming . Dynamic programming is a methodology useful for solving problems that involve taking decisions over several stages in a sequence. One thing common to all problems in this category is that current decisions influence both present & future periods.
Sequencing Theory . It is related to Waiting Line Theory. It is applicable when the facilities are fixed, but the order of servicing may be controlled. The scheduling of service or sequencing of jobs is done to minimize the relevant costs. For example, patients waiting for a series of tests in a hospital, aricrafts waiting for landing clearances, etc.
Replacement Models . These models are concerned with the problem of replacement of machines, individuals, capital assets, etc. due to their deteriorating efficiency, failure, or breakdown.
Markov Process. This process is used in situations where various states are defined and the system moves from one state to another on a probability basis. The probability of going from one state to another is known. This theory helps in calculating long run probability of being in a particular state.
Network Scheduling-PERT and CPM. Network scheduling is a technique used for planning, scheduling and monitoring large projects. Such large projects are very common in the field of construction, maintenance, computer system installation, research and development design, etc. Projects under network analysis are broken down into individual tasks, which are arranged in a logical sequence by deciding as to which activities should be performed simultaneously and which others sequentially.
Symbolic Logic. It deals with substituting symbols for words, classes of things, or functional systems. It incorporates rules, algebra of logic, and propositions. There have been only limited attempts to apply this technique to business problems; however, it is extensively used in designing computing machinery.
Information Theory. It is an analytical process transferred from the electrical communications field to operations research. It seeks to evaluate the effectiveness of information flow within a given system and helps in improving the communication flow.
Share This Article
Operations Research Simplified Back Next
Linear programming Simplex Method Transportation Problem Assignment Problem

IMAGES
COMMENTS
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations. Meaning of Assignment Problem: An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total ...
ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM Consider an assignment problem of assigning n jobs to n machines (one job to one machine). Let c ij be the unit cost of assigning ith machine to the jth job and,ith machine to jth job. Let x ij = 1 , if jth job is assigned to ith machine. x ij = 0 , if jth job is not assigned to ith machine. K.BHARATHI,SCSVMV. ASSIGNMENT ...
Operations Research - Definition and formulation of Assignment Problem | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research Posted On : 06.05.2019 12:29 am Chapter: 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
The document discusses assignment problems in operational research. An assignment problem aims to assign resources like machines or people to activities or jobs to minimize costs or maximize allocation points. It describes the mathematical formulation of assignment problems as linear programs that assign jobs to machines at minimum cost. Key differences from transportation problems are that ...
set of assignments, the assignments constitute an optimal solution • Optimal solution: • Machine 1 to location 4, Machine 2 to location 3, Machine 3 to location 1 [1] • Description • Mathematical model • Solution procedures • Hungarian algorithm • Transportation vs. Assignment problem Operations research I 14/32
Transportation and assignment models are special purpose algorithms of the linear programming. The simplex method of Linear Programming Problems(LPP) proves to be inefficient is certain situations like determining optimum assignment of jobs to persons, supply of materials from several supply points to several destinations and the like. More effective solution models have been evolved and these ...
2.1.1 Mathematical Formulation of Assignment Problem Consider the problem of assignment of a company which has n machines of different capacities for performing n different jobs and one machine can only be assigned to only one job. The objective is to minimize the total cost of assignment. The cost matrix for this problem is given in Table 2.1.
Operations Research (O.R.) is the application of advanced analytical methods to help make better decisions. Since its inception nearly 70 years ago, O.R. has contributed billions of dollars in benefits and savings to corporations, government, and the nonprofit sector. Operations Research is often concerned with determining the maximum (of profit,
The operations research expert has a wide array of methods and techniques available for solving problems. Linear Programming . Linear Programming (LP) is a mathematical technique of assigning a fixed amount of resources to satisfy a number of demands in such a way that some objective is optimized and other defined conditions are also satisfied.
Operations Research. Introduction & History of Operations Research. ... Assignment Problems. Assignment problem is a special type of linear programming problem. It deals in allocating the various ...