How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write a powerful thesis introduction.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.

Elements of a fantastic thesis introduction
Open with a (personal) story, begin with a problem, define a clear research gap, describe the scientific relevance of the thesis, describe the societal relevance of the thesis, write down the thesis’ core claim in 1-2 sentences, support your argument with sufficient evidence, consider possible objections, address the empirical research context, give a taste of the thesis’ empirical analysis, hint at the practical implications of the research, provide a reading guide, briefly summarise all chapters to come, design a figure illustrating the thesis structure.
An introductory chapter plays an integral part in every thesis. The first chapter has to include quite a lot of information to contextualise the research. At the same time, a good thesis introduction is not too long, but clear and to the point.
A powerful thesis introduction does the following:
- It captures the reader’s attention.
- It presents a clear research gap and emphasises the thesis’ relevance.
- It provides a compelling argument.
- It previews the research findings.
- It explains the structure of the thesis.
In addition, a powerful thesis introduction is well-written, logically structured, and free of grammar and spelling errors. Reputable thesis editors can elevate the quality of your introduction to the next level. If you are in search of a trustworthy thesis or dissertation editor who upholds high-quality standards and offers efficient turnaround times, I recommend the professional thesis and dissertation editing service provided by Editage .
This list can feel quite overwhelming. However, with some easy tips and tricks, you can accomplish all these goals in your thesis introduction. (And if you struggle with finding the right wording, have a look at academic key phrases for introductions .)
Ways to capture the reader’s attention
A powerful thesis introduction should spark the reader’s interest on the first pages. A reader should be enticed to continue reading! There are three common ways to capture the reader’s attention.
An established way to capture the reader’s attention in a thesis introduction is by starting with a story. Regardless of how abstract and ‘scientific’ the actual thesis content is, it can be useful to ease the reader into the topic with a short story.
This story can be, for instance, based on one of your study participants. It can also be a very personal account of one of your own experiences, which drew you to study the thesis topic in the first place.
Start by providing data or statistics
Data and statistics are another established way to immediately draw in your reader. Especially surprising or shocking numbers can highlight the importance of a thesis topic in the first few sentences!
So if your thesis topic lends itself to being kick-started with data or statistics, you are in for a quick and easy way to write a memorable thesis introduction.
The third established way to capture the reader’s attention is by starting with the problem that underlies your thesis. It is advisable to keep the problem simple. A few sentences at the start of the chapter should suffice.
Usually, at a later stage in the introductory chapter, it is common to go more in-depth, describing the research problem (and its scientific and societal relevance) in more detail.
You may also like: Minimalist writing for a better thesis
Emphasising the thesis’ relevance
A good thesis is a relevant thesis. No one wants to read about a concept that has already been explored hundreds of times, or that no one cares about.
Of course, a thesis heavily relies on the work of other scholars. However, each thesis is – and should be – unique. If you want to write a fantastic thesis introduction, your job is to point out this uniqueness!
In academic research, a research gap signifies a research area or research question that has not been explored yet, that has been insufficiently explored, or whose insights and findings are outdated.
Every thesis needs a crystal-clear research gap. Spell it out instead of letting your reader figure out why your thesis is relevant.
* This example has been taken from an actual academic paper on toxic behaviour in online games: Liu, J. and Agur, C. (2022). “After All, They Don’t Know Me” Exploring the Psychological Mechanisms of Toxic Behavior in Online Games. Games and Culture 1–24, DOI: 10.1177/15554120221115397
The scientific relevance of a thesis highlights the importance of your work in terms of advancing theoretical insights on a topic. You can think of this part as your contribution to the (international) academic literature.
Scientific relevance comes in different forms. For instance, you can critically assess a prominent theory explaining a specific phenomenon. Maybe something is missing? Or you can develop a novel framework that combines different frameworks used by other scholars. Or you can draw attention to the context-specific nature of a phenomenon that is discussed in the international literature.
The societal relevance of a thesis highlights the importance of your research in more practical terms. You can think of this part as your contribution beyond theoretical insights and academic publications.
Why are your insights useful? Who can benefit from your insights? How can your insights improve existing practices?

Formulating a compelling argument
Arguments are sets of reasons supporting an idea, which – in academia – often integrate theoretical and empirical insights. Think of an argument as an umbrella statement, or core claim. It should be no longer than one or two sentences.
Including an argument in the introduction of your thesis may seem counterintuitive. After all, the reader will be introduced to your core claim before reading all the chapters of your thesis that led you to this claim in the first place.
But rest assured: A clear argument at the start of your thesis introduction is a sign of a good thesis. It works like a movie teaser to generate interest. And it helps the reader to follow your subsequent line of argumentation.
The core claim of your thesis should be accompanied by sufficient evidence. This does not mean that you have to write 10 pages about your results at this point.
However, you do need to show the reader that your claim is credible and legitimate because of the work you have done.
A good argument already anticipates possible objections. Not everyone will agree with your core claim. Therefore, it is smart to think ahead. What criticism can you expect?
Think about reasons or opposing positions that people can come up with to disagree with your claim. Then, try to address them head-on.
Providing a captivating preview of findings
Similar to presenting a compelling argument, a fantastic thesis introduction also previews some of the findings. When reading an introduction, the reader wants to learn a bit more about the research context. Furthermore, a reader should get a taste of the type of analysis that will be conducted. And lastly, a hint at the practical implications of the findings encourages the reader to read until the end.
If you focus on a specific empirical context, make sure to provide some information about it. The empirical context could be, for instance, a country, an island, a school or city. Make sure the reader understands why you chose this context for your research, and why it fits to your research objective.
If you did all your research in a lab, this section is obviously irrelevant. However, in that case you should explain the setup of your experiment, etcetera.
The empirical part of your thesis centers around the collection and analysis of information. What information, and what evidence, did you generate? And what are some of the key findings?
For instance, you can provide a short summary of the different research methods that you used to collect data. Followed by a short overview of how you analysed this data, and some of the key findings. The reader needs to understand why your empirical analysis is worth reading.
You already highlighted the practical relevance of your thesis in the introductory chapter. However, you should also provide a preview of some of the practical implications that you will develop in your thesis based on your findings.
Presenting a crystal clear thesis structure
A fantastic thesis introduction helps the reader to understand the structure and logic of your whole thesis. This is probably the easiest part to write in a thesis introduction. However, this part can be best written at the very end, once everything else is ready.
A reading guide is an essential part in a thesis introduction! Usually, the reading guide can be found toward the end of the introductory chapter.
The reading guide basically tells the reader what to expect in the chapters to come.
In a longer thesis, such as a PhD thesis, it can be smart to provide a summary of each chapter to come. Think of a paragraph for each chapter, almost in the form of an abstract.
For shorter theses, which also have a shorter introduction, this step is not necessary.
Especially for longer theses, it tends to be a good idea to design a simple figure that illustrates the structure of your thesis. It helps the reader to better grasp the logic of your thesis.
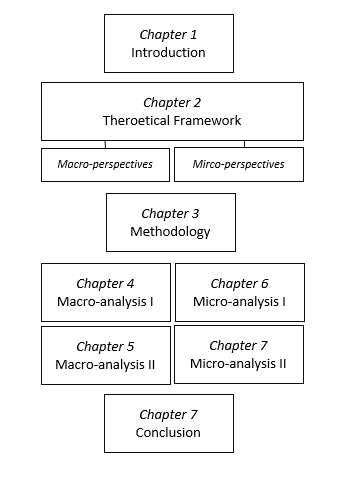
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The most useful academic social networking sites for PhD students
10 reasons not to do a master's degree, related articles.

Theoretical vs. conceptual frameworks: Simple definitions and an overview of key differences

How to deal with procrastination productively during thesis writing

How to write a unique thesis acknowledgement (+ FAQs)

75 linking words for academic writing (+examples)

Thesis Introduction
Ai generator.

After coming up with your desired topic for your thesis, it is about time that you began preparing that introduction. Just like every good speech or story, you need to have an introduction as to what your thesis outline is all about and what aspects your research will be covering.
In the introduction part of your thesis, you should be trying to focus on three main things, which are called Moves, according to the University of New South Wales database:

Move 1. E stablish your territory
By marking your territory, you begin to elaborate on what your topic is about and its present situation at hand. In doing so, there is also a need for you to point out that your area of research will only be limited to this scope, and for it to go beyond your area of responsibility would be out of the context. You may also see essay examples .
Move 2. E stablish a niche
This section is the heart and soul of your introduction. Without this, why was there even the need to conduct your research in the first place if you do not know what for?
Move 3. Introduce the current research
In conclusion to your introduction, this is where your research steps into the spotlight. In this part, you will be giving the panel a glimpse of the questions the researchers would be tackling during the course of the thesis journey. Aside from stating the hypotheses in this section, it is also important for the researchers to identify early on the end goals the study wants to achieve. You may also see thesis statement .
Each Move has a number of stages. Depending on what you need to say in your introduction, you might use one or more stages. You will also find examples of introductions, divided into stages with sample sentence extracts.
Most thesis introductions include some (but not all) of the stages listed below. There are variations between different schools and between different thesis, depending on the purpose of the thesis. You may also see essay writings .
Stages in a thesis introduction
- State the general topic and give some background.
- Provide a review of the literature related to the topic.
- Define the terms and scope of the topic.
- Outline the current situation.
- Evaluate the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages) and identify the gap.
- Identify the importance of the proposed research.
- State the research problem/questions.
- State the research aims and/or research objectives
- State the hypotheses.
- Outline the order of information in the thesis.
- Outline the methodology.
Listed below is a sample thesis introduction that was made by me and my partner during our college days. You may notice in the introduction, proponents of previous researchers who have conducted a similar study before since the opinion of experts gives the study basis and grounds as to why this topic requires more future studies. You may also see thesis proposal .
Introduction
Even as traditional media continues to be overshadowed by the insurmountable rise of electronic technology such as internet and mobile phones to access online information, daily newspapers have remained to be a key platform in disseminating public information which incites public discourse. A banner story of a newspaper is considered the highlight and most important news story of the day as newspapers follow an order of stories by arranging them of importance from front to inside pages (Tewksbury, 2002). You may also see personal essay .
At present, however, the media is confronted with issues such as making sensationalized, misleading, and satirical news stories not primarily to provide what the readers need to know, but rather to increase the issue’s marketability and compensate for the company’s production cost. Its gigantic headline running from corner to corner accompanied by its banner picture along with the story itself are put in place to draw readers’ attention and set the tone of the issue (Saxena, 2013). These existing practices greatly affect the placement of news stories from the most relevant and significant ones to the least leaving behind many substantial stories given less attention or least, under-reported. Moreover, this dilemma defeats the purpose of the main objectiveof journalism which is to provide the citizenry with information that is vital in shaping their realities and guide them in their decision making which then collates to a more systematic society. You may also see persuasive essay .
For instance, a local English daily placed the slain Bohol town mayor’s story, which reached national coverage, as its banner story of the issue while placing the progress of Cebu City’s Bus Rail Transit (BRT) project, which offers an opportunity for citizens to escape from the almost unmanageable metropolitan traffic jam when pushed through, in the latter pages of the issue. More so, with the long-aged flood problem in the metropolis especially during rainy season, a local English daily published on its second page an article entitled “Garganera: No program to solve flooding” due to the lack of comprehensive programs. You may also see short essay .
However, this did not land in the banner story, despite the relevance and the problem it seeks to raise; instead, a story about a landslide that killed two people was the highlight of the day. Hence, as it can be observed, politics, crime or disaster-based news which would likely create a stir among readers are most often than not picked as the banner story of the day. There are other news stories in other news categories that if written with the right angle and is deemed timely, can have its chance at the banner story. The news is a by-product of a journalist’s job of gathering enough evidence, conducting interviews and constant research in pursuit of the truth. In a newsroom, it is the editorial board that decides what news should be placed as the banner story which they perceive to be the most relevant news for the public to know. You may also see essay examples .
But sometimes, what the newspapers present as their banner story may not really align with the readers’ interests or perhaps may not strike as the most important or critical issue of the day. According to MacGregor (2007), journalists have been known to stray from their audiences in the context of traditional media. Gieber asserts (1960: 2004) that “news selection has no direct relationship to the wants of readers.” Gans (1979) further emphasizes Gieber’s point saying that journalists pay little to no attention to audience feedback, but place certain news together based on what they think would interest their audiences. You may also see reflective essay .
However, most, if not all of the reading public has no clue on how the editorial board decides each story’s position and inclusion. A proof of the abovementioned issues encompassing the news media industry is the presence of internal watchdogs that specialize on in-depth journalism to cover that under-reported news that is often overlooked by the mainstream news media. The Reuters Foundation is among those that provide the public with stories unlikely read or seen in the mainstream news such as humanitarian, women’s rights, human trafficking-based news. You may also see student essay .
One way or another, the media, in whatever form that it takes will never be perfect and will always be accused of bias and sensationalism which leads to public distrust. According to the analysis of some scholars, (Blumler and Gurevitch, 1995; McManus, 1994; Grabe et al., 2001) they have observed that the news is becoming more sensational or ‘tabloid-like’ over time. These kinds of stories may render the news more ‘colorful’ but are not exactly more informative (Blumler and Gurevitch, 1995; Franklin, 2005). You may also see analytical essay
Which is why one other end goal that the study wants to achieve is for each newspaper editorial board to be transparent on how the body decides each story should be written as well as the selection process of the news stories that determine which page each story belongs to. At the same time, it is also crucial that the public themselves understand how the editorial process is being done to grasp the concept behind story selection and editorial judgment in hopes that the strong trust between the public and the media will be restored once more as the media continues to deliver the news to the reading public with the challenge that they remain loyal and trustworthy by them.You may also see concept essay .
Only front-page studies are available for the researchers’ basis for their research as there were very minimal studies on banner stories. This study will be conducted for the purpose of understanding the present landscape of Cebu’s three local English newspapers. As compared to other media researchers, this will focus on identifying the most frequent news category published in the banner story of Cebu’s three local English newspapers: Cebu Daily News, SunStar Cebu, and The Freeman. Additionally, the researchers would also analyze the rhetoric of the dailies based on 1) the news values assigned by the journalists in every news story, and 2) the standard basis utilized by each newspaper’s editorial board in the selection process of news stories.You may also see comparative essay .
If you think the Introduction part of the thesis is exhausting, just wait until you get to the theoretical background and the review of related literature. They say those parts just crushes the soul out of you during the first half of your thesis writing. But do not fret. Because even though writing a thesis is like taking a walk in the park (Jurassic Park), all that hassle is really worth the tassel. Good luck!
Thesis Table Of Contents Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
- MS Publisher
Size: 36 KB
Thesis Proposal Template

Size: 80 KB
Thesis Proposal Gantt Chart Template

Size: 30 KB
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

How To Write A Thesis Introduction Chapter
Crafting the introductory chapter of a thesis can be confusing. If you are feeling the same, you are the at right place.
This post will explore how you can write a thesis introduction chapter, by outlining the essential components of a thesis introduction. We will look at the process, one section at a time, and explain them to help you get a hang of how to craft your thesis introduction.
How To Write A Good Thesis Introduction?
The opening section of a thesis introduction sets the stage for what’s to come, acting as a crucial hook to capture the reader’s attention.
Unlike the broader strokes found in the table of contents, this initial foray into your research is where you must distill the essence of your thesis into a potent, digestible form.
A skillful introduction begins with a concise preview of the chapter’s terrain, delineating the structure of the thesis with a clarity that avoids overwhelming the reader.
This is not the stage for exhaustive details; rather, it’s where you prime the reader with a snapshot of the intellectual journey ahead.
In crafting this segment, insiders advise adhering to a quartet of foundational sentences that offer an academic handshake to the reader.
First Section: I ntroduces the broad field of research, such as the significance of organisational skills development in business growth.
Second Section: Narrows the focus, pinpointing a specific research problem or gap — perhaps the debate on managing skill development in fast-paced industries like web development.
Third Section: Clearly state the research aims and objectives, guiding the reader to the ‘why’ behind your study. Finally, a sentence should outline the roadmap of the introduction chapter itself, forecasting the background context, research questions, significance, and limitations that will follow.
Such a calibrated approach ensures that every element from the research objective to the hypothesis is presented with precision.
This method, a well-guarded secret amongst seasoned researchers, transforms a mundane introduction into a compelling entrée into your dissertation or thesis.
Background To The Study
This section sets the tone for the research journey ahead. The goal here is to capture the reader’s attention by threading relevant background information into a coherent narrative that aligns with the research objectives of the thesis.
To write a good thesis introduction, one must carefully describe the background to highlight the context in which the research is grounded.
This involves not just a literature review but a strategic presentation of the current state of research, pinpointing where your work will wedge itself into the existing body of knowledge.
For instance, if the research project focuses on qualitative changes in urban planning, the introduction should spotlight key developmental milestones and policy shifts that foreground the study’s aims and objectives.
When writing this section, articulate the focus and scope of the research, ensuring the reader grasps the importance of the research questions and hypothesis.
This section must not only be informative but also engaging. By the end of the introductory chapter, the reader should be compelled to continue reading, having grasped a clear and easy-to-understand summary of each chapter that will follow.
It’s a good idea to address frequently asked questions and to clearly state any industry-specific terminology, assuming no prior expertise on the reader’s part.
This approach establishes a solid foundation for the rest of the thesis or dissertation, ensuring the reader is well-prepared to dive into the nuances of your research project.
Research Problem
Crafting the nucleus of your thesis or dissertation hinges on pinpointing a compelling research problem. This step is crucial; it is the keystone of a good thesis introduction chapter, drawing the reader’s attention and setting the stage for the rest of your thesis.

A well-defined research problem addresses a gap in the existing literature, underscored by a qualitative or quantitative body of research that lacks consensus or is outdated, especially in rapidly evolving fields.
Consider the dynamic sphere of organizational skills development. Established research might agree on strategies for industries where skills change at a snail’s pace.
However, if the landscape shifts more quickly—take web development for example, where new languages and platforms emerge incessantly—the literature gap becomes evident.
Herein lies the research problem: existing strategies may not suffice in industries characterized by a swift knowledge turnover.
When writing your introduction, your goal is to clearly state this gap. A great thesis introduction delineates what is known, what remains unknown, and why bridging this chasm is significant.
It should illuminate the research objectives and questions, laying out a roadmap for the reader in a language that’s clear and easy to understand, regardless of their familiarity with the topic.
You’ll be able to capture and maintain the reader’s interest by effectively communicating why your research matters—setting the scene for your hypothesis and subsequent investigation.
Remember, a good thesis introduction should not only provide background information but also articulate the focus and scope of the study, offering a preview of the structure of your thesis.
Research Aims, Objectives And Questions
This pivotal section lays out the foundation by providing relevant background information, but it is the articulation of research aims, objectives, and questions that clarifies the focus and scope of your study.
The research aim is the lighthouse of your thesis, illuminating the overarching purpose of your investigation.
For instance, a thesis exploring skills development in fast-paced industries might present an aim to evaluate the effectiveness of various strategies within UK web development companies. This broad goal sets the direction for more detailed planning.
Research objectives drill down into specifics, acting as stepping stones toward achieving your aim. They are the tangible checkpoints of your research project, often action-oriented, outlining what you will do.
Examples might include identifying common skills development strategies or evaluating their effectiveness. These objectives segment the monumental task into manageable portions, offering a clear and easy way to write a structured pathway for the research.

Equally critical are the research questions, which translate your objectives into inquiries that your thesis will answer. They narrow the focus even further, dictating the structure of the thesis.
For instance:
- “What are the prevalent skills development strategies employed by UK web development firms?”
- “How effective are these strategies?”
Such questions demand concrete responses and guide the reader through the rest of the thesis.
Significance Of The Study
The “Significance of the Study” section within the introduction chapter of your thesis or dissertation holds considerable weight in laying out the importance of your research.

This segment answers the pivotal question: “Why does this research matter?” It is strategically placed after the background information and literature review to underscore the contribution your study makes to the existing body of research.
In writing this section, you’ll be able to capture the reader’s attention by clearly stating the impact and added value your research project offers.
Whether it’s a qualitative or quantitative study, the significance must be articulated in terms of:
- Theoretical
- Academic, and
- Societal contributions.
For instance, it may fill gaps identified in the literature review, propose innovative solutions to pressing problems, or advance our understanding in a certain field.
A good thesis introduction will succinctly convey three main things: the research objective, the hypothesis or research questions, and the importance of your research.
It’s a good idea to provide your reader with a roadmap, foreshadowing the structure of the thesis and offering a summary of each chapter, thus enticing the reader to continue reading.
When you write the introduction section, it should also serve as a concise synopsis of the focus and scope of your research.
It’s often beneficial to include examples of introductions that clearly state the research objectives and questions, offering a snapshot of the whole thesis, and setting the stage for the rest of your thesis.
Limitations Of The Study
A thorough thesis introduction lays out specific research objectives and questions, yet it also sheds light on the study’s inherent boundaries. This is the purpose of the Limitation of The Study section.
The limitations section is not a confession of failure; instead, it’s a good idea to see it as demonstrating academic maturity.
Here, you clearly state the parameters within which the research was conducted.
For instance, a qualitative study might face scrutiny for subjectivity, or a quantitative one for potentially oversimplifying complexities. Other common constraints include the scope—perhaps focusing on a narrow aspect without considering variable interplay—resources, and generalizability.
For example, a study concentrated on a specific industry in Florida may not hold water in a different context, for example in Tokyo, Japan.
It’s essential to write this section with transparency. A good thesis introduction doesn’t shy away from limitations. Instead, it captures the reader’s attention by laying them out systematically, often in a dedicated paragraph for each chapter.
This honesty allows the reader to understand the research’s focus and scope while providing a clear and easy-to-follow structure of the thesis.
This approach also serves to manage the reader’s expectations. By preempting frequently asked questions about the scope of your research, the introductory chapter establishes a trust that encourages the reader to continue reading, aware of the contours shaping the body of research.
Thus, a well-articulated limitations section is not just part of the thesis; it is an integral piece of a responsibly woven research narrative.
Structural Outline Of Thesis, Thesis Statement
Within the thesis or dissertation, the structural outline section is akin to a compass, orienting the reader’s journey through the academic landscape laid out within the pages.
Crafting this section is a strategic exercise, one that requires an understanding of the work’s skeleton.
In essence, it’s the blueprint for the construction of a scholarly argument, and writing a good thesis necessitates a clear and easy-to-follow outline.
When you write a thesis outline, it’s not only about catching the reader’s attention; it’s also about holding it throughout the rest of the thesis.
This is where the structural outline comes into play, often beginning with an introduction chapter that presents the thesis statement, research objectives, and the importance of your research.
Following the introduction, a typical outline might proceed with Chapter 2, offering a literature review to acquaint the reader with existing literature and how this piece of research fits within it.
Subsequent chapters, each with a paragraph in the outline, detail the methodological approach—whether it’s qualitative or quantitative—and the research’s focus and scope.
A well-thought-out outline should also preview the structure of the thesis, succinctly:
- Summarizing the main aim and objectives of each chapter, and
- Indicating the type of data and analysis that will be presented.
This roadmap reassures the reader that the dissertation or thesis will cover the necessary ground in a logical progression, continuing from where the introduction first captivated their interest.
The structural outline is not only part of the thesis—it’s a strategic framework that informs the reader what to expect in each subsequent chapter.
Done correctly, this section allows the reader to understand the whole thesis in a nutshell and can often serve as a checklist for both the reader and the writer.
This ensures that the key stages of the research project are clearly stated and that the reader is provided with a roadmap to guide them through the detailed landscape of your scholarly work.
Write An Introduction Chapter With Ease
Mastering the thesis introduction chapter is a critical step towards a successful dissertation. It’s about striking a balance between engagement and information, presenting a snapshot of your research with clarity and intrigue.
Remember to start with a hook, establish the context, clarify your aims, and highlight the significance, all while being mindful of the study’s scope and limitations.
By adhering to these principles, your introduction will not only guide but also inspire your readers, laying a strong foundation for the in-depth exploration that follows in your thesis or dissertation.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

- AI Detector and Humanizer
- Business Solutions
- Try it Free
How to Write a Thesis Introduction (with Examples)

As Ralph Waldo Emerson once said, “Sometimes a scream is better than a thesis.” While it’s ironically the case for many, writing a thesis is basically the culmination of your hard work.
There’s a certain pride in accomplishing such a task, and many people hold it close to their hearts throughout their lifetimes.
This showcases a student’s ability to contribute original insights to their field and opens many more doors to broaden their academic and professional opportunities. Finishing a thesis certainly has weight.
The great thing about education today is that technology can help make things easier. AI tools, for instance, can assist with writing research papers and doing thesis work.
Even teachers can utilize the power of AI to improve their ways of teaching – but more on the exciting AI stuff later.
What you need to start with for your thesis is to create a strong introduction. Your thesis intro sets the tone for your entire work, so getting it right is important.
Here’s everything you need to know on how to write a thesis introduction that instantly catches the eye and informs effectively at a glance.
What Types of Information Should Be Included in Your Thesis Introduction?
After days and nights of researching, typing, and editing, the general average thesis length ends up at around 20-50 pages.
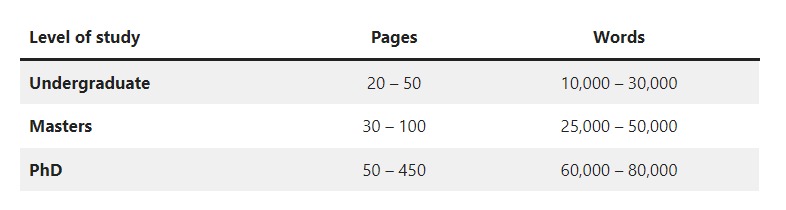
A PhD dissertation, usually tougher, can go up to 90-500 pages long. That’s a lot of work.
With so much information to showcase, your thesis intro should be able to make a big impression. A weak introduction can mislead your readers and even diminish the value of your entire thesis.

Never Worry About AI Detecting Your Texts Again. Undetectable AI Can Help You:
- Make your AI assisted writing appear human-like.
- Bypass all major AI detection tools with just one click.
- Use AI safely and confidently in school and work.
As the first impression of your work, the intro sets the stage by providing some context, highlighting the research problem, and laying out your objectives clearly.
It can be intimidating just thinking about it, so we’re here to make sure your thesis intro delivers the punch it needs. Here are some things that you should include.
Have an attention-grabbing opening
In the marketing world, you’ve only got eight seconds to grab a customer’s attention; that’s the average attention span.
While your teacher won’t drop your thesis if your introduction doesn’t grab them within seconds, having a great opening can still make a strong impact.
The main goal here is to present a compelling hook that sparks curiosity.
Include a surprising statistic, engage with a thought-provoking question, share a short but relatable anecdote, or try to be daring and make a bold statement that shocks but relates to your research topic.
There are many ways to do it, but ultimately, you want to engage your reader right from the start.
Provide context and the importance of the topic
“In this thesis, we will be exploring the effects of social media on communication.” Why, though? And what part of social media are we talking about here?
This is a bad example of a thesis intro because it lacks context.
Instead of simply choosing a controversial or topical subject to make an impact, you need to go deeper straight away.
The goal of providing context is to guide your reader in understanding why your topic is worth discussing in the first place.
You can offer a brief overview of already existing research and how you can add to it, and also show the gaps and unresolved issues that your study aims to fix.
Highlighting your topic goes to show that it’s an important matter to discuss in your field.
Engage through specific questions that your research addresses
One of the best ways to make your thesis intro stand out is by asking specific questions.
For example, if your research is about the effects of social media on traditional media, rather than just stating it outright, you can start off with an engaging question like “Is social media ending the age of the newspaper?”
In this way, you instantly grab the attention of your reader with a compelling question while still providing a sense of what your research will be about.
It’s a two-punch combo of showing immediate purpose and relevance while making your thesis intro easy to follow.
Frame your research in the form of specific and engaging questions so you can lay the groundwork for a more focused thesis.
Thesis Introduction Tips

So far, a good thesis introduction should be able to outline the main topic clearly, present some compelling questions, and provide context and significance for the study.
It’s definitely not easy, but there are ways to make it more doable. Here are some handy thesis introduction tips to help you out.
Know your audience
Knowing your audience means that you understand who will be reading your thesis. By doing this, you can create an introduction that meets their expectations and interests.
When writing a thesis intro, you should be able to consider the background, knowledge level, and interests of the thesis readers – your advisor, committee members, and other related academics.
Knowing this, you can set the right tone, which is usually formal, and engage in a way that interests them.
Refer to your thesis proposal or notes
If you want to make a seamless thesis paper, you will constantly need to refer to your proposal and notes.
You should refer to all the preliminary work that you’ve done to direct the writing of your introduction.
This can include your research questions, objectives, literature review, and methodology that you’ve outlined for your proposal.
It’s always important to go back and review your thesis notes regularly because these help you:
- Ensure that your thesis introduction is consistent with your original proposal.
- Present the main elements of your research.
- Organize your thoughts and create a well-structured introduction, contributing to your overall thesis flow.
Keep your thesis proposal and notes by your side. They will help you create a strong introduction that provides clear context for your research.
Use Assistant AI tools to help with writing and proofreading
Especially when it comes to writing, AI tools have become quite useful.
You might already be familiar with ChatGPT, which uses advanced algorithms to generate the needed content; it can even proofread text .
AI tools can be useful to writers and researchers by offering suggestions and writing parts of the work that they can improve later.
This makes the writing process a whole lot more efficient and much less time-consuming. With AI, you can essentially produce high-quality work under tight deadlines.
However, while AI tools are clearly helpful, it’s necessary that you still use them responsibly.
AI plagiarism is a growing concern that happens when any AI-generated content is presented as original work without giving the right acknowledgment.
This can severely damage the credibility of your research and even get you in trouble.
Treat AI as what it’s intended to be – a tool – rather than the main writer of your work. You should still be the writer of your own work.
To avoid any issue with AI, a reliable detector like Undetectable AI can be used to always make sure that your content passes as human-written.
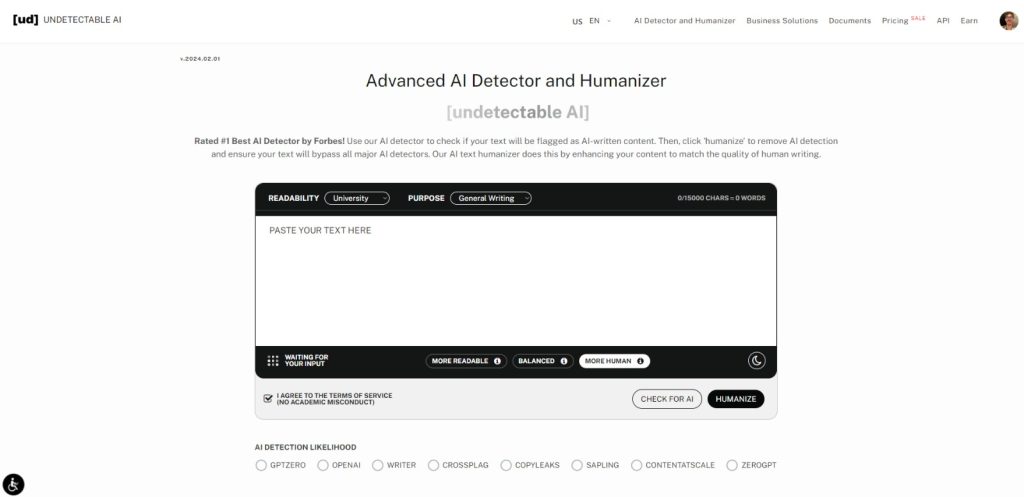
Undetectable analyzes any text you submit to effectively detect AI content. It also includes features like a humanizer that adjusts the writing to match a natural human tone .
We certainly don’t want to stop you from maximizing your potential with the help of AI, so with a useful AI detector and humanizer by your side, you can always get the results you want.
You can try Undetectable AI easily with the widget below (English only). Just input your text and see how it can transform your writing!
Make sure you clearly state your topic, aims, and objectives
This one is essential. Your thesis introduction should be able to clearly define what your research is about (topic), what you plan to accomplish (aims), and the steps you’re taking to get there (objectives).
It’s pretty straightforward and is a no-brainer, but you must do this for several reasons:
- Helps your readers understand the focus of your research right from the get-go.
- Sets clear expectations for your thesis.
- Establishes relevance, making your work highly credible.
- Easier assessment (whether you’ve achieved your goals) by your advisor and evaluators.
Remember, a well-defined introduction is your first step toward a successful thesis. Make it matter.
Explain why your research matters
If your thesis doesn’t make an impact in your field, then it might not be seen as valuable. So, from the start, be sure to explain why your research matters.
This provides a basis for why you’re choosing a specific topic in the first place and explaining why it deserves their attention.
To help, you can also link your research to real-world applications or social issues to enhance its appeal to the research community and beyond.
3 Thesis Introduction Examples to Inspire You

Writing a thesis introduction can be quite a challenge, but looking at examples can help you understand how to start your research on the right foot.
Communications Example
“Is social media ending the age of the newspaper?” This question frequently arises in discussions as the communication landscape continuously evolves.
Platforms like Facebook, X (previously called Twitter), and Instagram continue to grow, and their impact on traditional media – newspapers, television, and radio – becomes more significant and complex.
Social media has drastically changed how people access information. Unlike traditional media, which professional journalists and editors usually produce, social media allows anyone to create and share content.
This shift has huge implications for both media producers and consumers. Understanding these changes is important for professionals in the field and the general population.
This thesis aims to answer several questions: How has social media affected the credibility of traditional news sources?
What strategies are traditional media adopting to compete in a digital world? And how do today’s audiences perceive news found on social media vs traditional platforms?
By addressing these questions, this research seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current media landscape and provide some discourse on the future of communication and modern-day responsible journalism.
Environmental Science Example
Food production is one of the largest contributors to environmental damage.
The methods that we traditionally use to grow and raise our food have serious implications for resource use, greenhouse gas emissions, and land use.
So, we ask the question, “Can our food choices save the planet?”
As global populations rise and climate change accelerates, understanding the environmental impact of different food production systems has never been more important.
Plant-based agriculture and animal-based agriculture differ considerably, so studying these differences can help identify sustainable practices that minimize and ultimately prevent environmental damage.
This thesis aims to address how plant-based and animal-based food production systems compare in terms of resource use and environmental impact and what practices within these systems can reduce their impact on the environment.
Education Example
The global pandemic has made a dent in how we live, and that includes the state of education.
During this difficult time, schools and universities worldwide were essentially forced to shift to online learning almost overnight.
This sudden and widespread adoption of online learning presents a unique opportunity to assess its effectiveness and impact on education – past the pandemic.
If online learning is actually shown to be effective, it could lead to more flexible, accessible, and inclusive educational practices.
Conversely, if notable shortcomings are identified, this can highlight areas that need improvement to support students and educators better.
This thesis aims to identify the effectiveness of online learning in achieving educational outcomes compared to traditional classroom settings, the major challenges faced by students and educators during this transition, and how factors such as socioeconomic status and access to technology influence the effectiveness of online learning.
With this study, we can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of online education, contributing to the broader discussion of post-pandemic learning.
How do you start an introduction for a thesis?
To start a thesis introduction, start with a hook that draws the reader in and sets the stage for your research topic. Provide context by discussing the significance of the topic. Then transition into your thesis statement, which outlines the main argument or purpose of your research.
What is an example of a thesis statement in an introduction?
An example of a thesis statement in an introduction could be: “This thesis examines how social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and X (formerly Twitter) have reshaped how individuals interact and form relationships in the digital age, with an emphasis on interpersonal communication.” Clearly state the main focus and purpose of your research and provide a roadmap for the reader to understand what will be discussed in your thesis.
What is a good way to start a thesis statement?
You could start a thesis statement by introducing your topic and talking about the specific angle you plan to explore in your research. Grab the reader’s attention and establish why it’s worth investigating further.
How do you start writing a thesis?
Writing a thesis starts with choosing a topic that interests you – and then aligns with your field. Be sure that the main goal of your thesis stays relevant to gain some credibility. With this, you can create a clear thesis statement that outlines the main objective of your study. This is where you can start drafting a compelling thesis introduction and then filling your content with strong arguments that are supported by evidence and analysis. Firmly conclude with a summary of your findings and their implications. Always cite your sources accurately and follow the academic guidelines.
Maximizing the potential of your thesis always starts with an introduction, and with the help of AI tools, you can be confident to write a strong one.
When using these tools, just be sure to have Undetectable AI by your side so that any content you need assistance with stays authentic.
The humanizer feature matches real human writing styles as closely as possible so that your content speaks to your readers.
Remember to tailor your thesis introduction to your specific research topic and audience, and use examples and evidence to back up your claims.
With these strategies in mind, you’ll be well-equipped to write an impactful thesis introduction – paving the way for a great thesis.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a good thesis introduction

1. Identify your readership
2. hook the reader and grab their attention, 3. provide relevant background, 4. give the reader a sense of what the paper is about, 5. preview key points and lead into your thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a good thesis introduction, related articles.
Many people struggle to write a thesis introduction. Much of your research prep should be done and you should be ready to start your introduction. But often, it’s not clear what needs to be included in a thesis introduction. If you feel stuck at this point not knowing how to start, this guide can help.
Tip: If you’re really struggling to write your thesis intro, consider putting in a placeholder until you write more of the body of your thesis. Then, come back to your intro once you have a stronger sense of the overall content of your thesis.
A good introduction draws readers in while providing the setup for the entire project. There is no single way to write an introduction that will always work for every topic , but the points below can act as a guide. These points can help you write a good thesis introduction.
Before even starting with your first sentence, consider who your readers are. Most likely, your readers will be the professors who are advising you on your thesis.
You should also consider readers of your thesis who are not specialists in your field. Writing with them in your mind will help you to be as clear as possible; this will make your thesis more understandable and enjoyable overall.
Tip: Always strive to be clear, correct, concrete, and concise in your writing.
The first sentence of the thesis is crucial. Looking back at your own research, think about how other writers may have hooked you.
It is common to start with a question or quotation, but these types of hooks are often overused. The best way to start your introduction is with a sentence that is broad and interesting and that seamlessly transitions into your argument.
Once again, consider your audience and how much background information they need to understand your approach. You can start by making a list of what is interesting about your topic:
- Are there any current events or controversies associated with your topic that might be interesting for your introduction?
- What kinds of background information might be useful for a reader to understand right away?
- Are there historical anecdotes or other situations that uniquely illustrate an important aspect of your argument?
A good introduction also needs to contain enough background information to allow the reader to understand the thesis statement and arguments. The amount of background information required will depend on the topic .
There should be enough background information so you don't have to spend too much time with it in the body of the thesis, but not so much that it becomes uninteresting.
Tip: Strike a balance between background information that is too broad or too specific.
Let the reader know what the purpose of the study is. Make sure to include the following points:
- Briefly describe the motivation behind your research.
- Describe the topic and scope of your research.
- Explain the practical relevance of your research.
- Explain the scholarly consensus related to your topic: briefly explain the most important articles and how they are related to your research.
At the end of your introduction, you should lead into your thesis statement by briefly bringing up a few of your main supporting details and by previewing what will be covered in the main part of the thesis. You’ll want to highlight the overall structure of your thesis so that readers will have a sense of what they will encounter as they read.
A good introduction draws readers in while providing the setup for the entire project. There is no single way to write an introduction that will always work for every topic, but these tips will help you write a great introduction:
- Identify your readership.
- Grab the reader's attention.
- Provide relevant background.
- Preview key points and lead into the thesis statement.
A good introduction needs to contain enough background information, and let the reader know what the purpose of the study is. Make sure to include the following points:
- Briefly describe the motivation for your research.
The length of the introduction will depend on the length of the whole thesis. Usually, an introduction makes up roughly 10 per cent of the total word count.
The best way to start your introduction is with a sentence that is broad and interesting and that seamlessly transitions into your argument. Consider the audience, then think of something that would grab their attention.
In Open Access: Theses and Dissertations you can find thousands of recent works. Take a look at any of the theses or dissertations for real-life examples of introductions that were already approved.


🚀 Work With Us
Private Coaching
Language Editing
Qualitative Coding
✨ Free Resources
Templates & Tools
Short Courses
Articles & Videos
Dissertation Writing 101: The Introduction

I f you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: Writing The Introduction Chapter
- The purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis
A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.

Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.
#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.

#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have .
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
47 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Hi Derek, your article has been really helpful. Samuel. Student, Masters in Communication and Development Studies. Papua New Guinea University of Technology. 2024.
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
You explain what moment in life caused you to have a peaked interest in the thesis topic. Personal experiences? Or something that had an impact on your life, or others. Something would have caused your drive of topic. Dig deep inside, the answer is within you!
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
This is great!
Thank you for all this information. I feel very confident to complete my dissertation with all the help given. This is awesome and very helpful; I was studying alone with very little supervision and feedback of my thoughts. feelings. aspirations and experiences, with my topic or Kaupapa. It is a topic that very little or few researchers have written a thesis about (from personal experiences). As John Burke said ” unless you are sitting in the front seat and row, up close and personal, you will not understand the difficulties of growing up and living with hearing loss (caused by swimmer’s ears infection, resulting in burst eardrums, unless one denies having a hearing loss. This is from a Māori woman’s cultural perspective. Nga mihi nui kia koutou.
Thanks a lot for this information. The concepts are explained in a simple yet powerful way. They are easy to understand and adopt. Your team played an important role in writing my thesis. A big thank you !!!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

How to Write the Thesis Or Dissertation Introduction – Guide
Published by Carmen Troy at August 31st, 2021 , Revised On June 7, 2024
What would you tell someone if they asked you to introduce yourself? You’d probably start with your name, what you do for a living…etc., etc., etc. Think of your dissertation as the same. How would you go about it if you had to introduce it to the world for the first time?
Keep this forefront in your mind for the remainder of this guide: you are introducing your research to the world that doesn’t even know it exists. Every word, phrase and line you write in your introduction will stand for the strength of your dissertation’s character.
This is not very different from how, in real life, if someone fails to introduce themselves properly (such as leaving out what they do for a living, where they live, etc.) to a stranger, it leaves a lasting impression on the stranger.
Don’t leave your dissertation a stranger among other strangers. Let’s review the little, basic concepts we already have at the back of our minds, perhaps, to piece them together in one body: an introduction.
What Goes Inside an Introduction
The exact ingredients of a dissertation or thesis introduction chapter vary depending on your chosen research topic, your university’s guidelines, and your academic subject – but they are generally mixed in one sequence or another to introduce an academic argument.
The critical elements of an excellent dissertation introduction include a definition of the selected research topic , a reference to previous studies on the subject, a statement of the value of the subject for academic and scientific communities, a clear aim/purpose of the study, a list of your objectives, a reference to viewpoints of other researchers and a justification for the research.
Steps of Writing a Dissertation Introduction
- Research background
- Significance of the research
- Research problem
- Research questions
- The research aims and objectives
- Limitations of the research
- Outline of dissertation
1. Research Background – Writing a Dissertation Introduction
This is the very first section of your introduction. Building a background of your chosen topic will help you understand more about the topic and help readers know why the general research area is problematic, interesting, central, important, etc.
Your research background should include significant concepts related to your dissertation topic. This will give your supervisor and markers an idea that you’ve investigated the research problem thoroughly and know the various aspects of your topic.
The introduction to a dissertation shouldn’t talk only about other research work in the same area, as this will be discussed in the literature review section. Moreover, this section should not include the research design and data collection method(s) .
All about research strategy should be covered in the methodology chapter . Research background only helps to build up your research in general.
For instance, if your research is based on job satisfaction measures of a specific country, the content of the introduction chapter will generally be about job satisfaction and its impact.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- Never resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements

2. Significance of the Research
As a researcher, you must demonstrate how your research will provide value to the scientific and academic communities. If your dissertation is based on a specific company or industry, you need to explain why that industry and company were chosen.
If you’re comparing, explain why you’re doing so and what this research will yield. Regardless of your chosen research topic, explain thoroughly in this section why this research is being conducted and what benefits it will serve.
The idea here is to convince your supervisor and readers that the concept should be researched to find a solution to a problem.
3. Research Problem
Once you’ve described the main research problem and the importance of your research, the next step would be to present your problem statement , i.e., why this research is being conducted and its purpose.
This is one of the essential aspects of writing a dissertation’s introduction. Doing so will help your readers understand what you intend to do in this research and what they should expect from this study.
Presenting the research problem competently is crucial in persuading your readers to read other parts of the dissertation paper . This research problem is the crux of your dissertation, i.e., it gives a direction as to why this research is being carried out, and what issues the study will consider. The research problem should be a clear and concise statement that identifies the gap in the existing knowledge that your research aims to fill. It should be specific enough to guide your research, but broad enough to allow for a comprehensive investigation.
For example, if your dissertation is based on measuring the job satisfaction of a specific organisation, your research problem should talk about the problem the company is facing and how your research will help the company to solve that.
If your dissertation is not based on any specific organisation, you can explain the common issues that companies face when they do not consider job satisfaction as a pillar of business growth and elaborate on how your research will help them realise its importance.
Citing too many references in the introduction chapter isn’t recommended because here, you must explain why you chose to study a specific area and what your research will accomplish. Any citations only set the context, and you should leave the bulk of the literature for a later section.
4. Research Question(s)
The central part of your introduction is the research question , which should be based on your research problem and the dissertation title. Combining these two aspects will help you formulate an exciting yet manageable research question. Your research question is what your research aims to answer and around which your dissertation will revolve. The research question should be specific and concise.
Your research question is what your research aims to answer and around which your dissertation will revolve. The research question should be specific and concise.
It should be a one- or two-line question you’ve set out to answer through your dissertation. For the job satisfaction example, a sample research question could be, how does job satisfaction positively impact employee performance?
Look up dissertation introduction examples online or ask your friends to get an idea of how an ideal research question is formed. Or you can review our dissertation introduction example here and research question examples here .
Once you’ve formed your research question, pick out vital elements from it, based on which you will then prepare your theoretical framework and literature review. You will come back to your research question again when concluding your dissertation .
Sometimes, you might have to formulate a hypothesis in place of a research question. The hypothesis is a simple statement you prove with your results , discussion and analysis .
A sample hypothesis could be job satisfaction is positively linked to employee job performance . The results of your dissertation could be in favour of this dissertation or against it.
Tip: Read up about what alternative, null, one-tailed and two-tailed hypotheses are so you can better formulate the hypothesis for your dissertation. Following are the definitions for each term, as retrieved from Trochim et al.’s Research Methods: The Essential Knowledge Base (2016):
- Alternative hypothesis (H 1 ): “A specific statement of prediction that usually states what you expect will happen in your study.”
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): “The hypothesis that describes the possible outcomes other than the alternative hypothesis. Usually, the null hypothesis predicts there will be no effect of a program or treatment you are studying.”
- One-tailed hypothesis: “A hypothesis that specifies a direction; for example, when your hypothesis predicts that your program will increase the outcome.”
- Two-tailed hypothesis: “A hypothesis that does not specify a direction. For example, if you hypothesise that your program or intervention will affect an outcome, but you are unwilling to specify whether that effect will be positive or negative, you are using a two-tailed hypothesis.”
Get Help with Any Part of Your Dissertation!
UK’s best academic support services. How would you know until you try?
Interesting read: 10 ways to write a practical introduction fast .
Get Help With Any Part of Your Dissertation!
Uk’s best academic support services. how would you know until you try, 5. research aims and objectives.
Next, the research aims and objectives. Aims and objectives are broad statements of desired results of your dissertation . They reflect the expectations of the topic and research and address the long-term project outcomes.
These statements should use the concepts accurately, must be focused, should be able to convey your research intentions and serve as steps that communicate how your research question will be answered.
You should formulate your aims and objectives based on your topic, research question, or hypothesis. These are simple statements and are an extension of your research question.
Through the aims and objectives, you communicate to your readers what aspects of research you’ve considered and how you intend to answer your research question.
Usually, these statements initiate with words like ‘to explore’, ‘to study’, ‘to assess’, ‘to critically assess’, ‘to understand’, ‘to evaluate’ etc.
You could ask your supervisor to provide some thesis introduction examples to help you understand better how aims and objectives are formulated. More examples are here .
Your aims and objectives should be interrelated and connect to your research question and problem. If they do not, they’ll be considered vague and too broad in scope.
Always ensure your research aims and objectives are concise, brief, and relevant.
Once you conclude your dissertation , you will have to revert back to address whether your research aims and objectives have been met.
You will have to reflect on how your dissertation’s findings , analysis, and discussion related to your aims and objectives and how your research has helped in achieving them.
6. Research Limitations
This section is sometimes a part of the dissertation methodology section ; however, it is usually included in the introduction of a dissertation.
Every research has some limitations. Thus, it is normal for you to experience certain limitations when conducting your study.
You could experience research design limitations, data limitations or even financial limitations. Regardless of which type of limitation you may experience, your dissertation would be impacted. Thus, it would be best if you mentioned them without any hesitation.
When including this section in the introduction, make sure that you clearly state the type of constraint you experienced. This will help your supervisor understand what problems you went through while working on your dissertation.
However, one aspect that you should take care of is that your results, in no way, should be influenced by these restrictions. The results should not be compromised, or your dissertation will not be deemed authentic and reliable.
After you’ve mentioned your research limitations, discuss how you overcame them to produce a perfect dissertation .
Also, mention that your limitations do not adversely impact your results and that you’ve produced research with accurate results the academic community can rely on.
Also read: How to Write Dissertation Methodology .
7. Outline of the Dissertation
Even though this isn’t a mandatory sub-section of the introduction chapter, good introductory chapters in dissertations outline what’s to follow in the preceding chapters.
It is also usual to set out an outline of the rest of the dissertation . Depending on your university and academic subject, you might also be asked to include it in your research proposal .
Because your tutor might want to glance over it to see how you plan your dissertation and what sections you’d include; based on what sections you include and how you intend to research and cover them, they’d provide feedback for you to improve.
Usually, this section discusses what sections you plan to include and what concepts and aspects each section entails. A standard dissertation consists of five sections : chapters, introduction, literature review , methodology , results and discussion , and conclusion .
Some dissertation assignments do not use the same chapter for results and discussion. Instead, they split it into two different chapters, making six chapters. Check with your supervisor regarding which format you should follow.
When discussing the outline of your dissertation , remember that you’d have to mention what each section involves. Discuss all the significant aspects of each section to give a brief overview of what your dissertation contains. This is precisely what our dissertation outline service provides.
Writing a dissertation introduction might seem complicated, but it is not if you understand what is expected of you. To understand the required elements and make sure that you focus on all of them.
Include all the aspects to ensure your supervisor and other readers can easily understand how you intend to undertake your research.
“If you find yourself stuck at any stage of your dissertation introduction, get introduction writing help from our writers! At ResearchProspect, we offer a dissertation writing service , and our qualified team of writers will also assist you in conducting in-depth research for your dissertation.
Topic Discussion versus Topic Introduction
Discussing and introducing a topic are two highly different aspects of dissertation introduction writing. You might find it easy to discuss a topic, but introducing it is much trickier.
The introduction is the first thing a reader reads; thus, it must be to the point, informative, engaging, and enjoyable. Even if one of these elements is missing, the reader will not be motivated to continue reading the paper and will move on to something different.
So, it’s critical to fully understand how to write the introduction of a dissertation before starting the actual write-up.
When writing a dissertation introduction, one has to explain the title, discuss the topic and present a background so that readers understand what your research is about and what results you expect to achieve at the end of the research work.
As a standard practice, you might work on your dissertation introduction chapter several times. Once when you’re working on your proposal and the second time when writing your actual dissertation.
“Want to keep up with the progress of the work done by your writer? ResearchProspect can deliver your dissertation order in three parts; outline, first half, and final dissertation delivery. Here is the link to our online order form .
Many academics argue that the Introduction chapter should be the last section of the dissertation paper you should complete, but by no means is it the last part you would think of because this is where your research starts from.
Write the draft introduction as early as possible. You should write it at the same time as the proposal submission, although you must revise and edit it many times before it takes the final shape.
Considering its importance, many students remain unsure of how to write the introduction of a dissertation. Here are some of the essential elements of how to write the introduction of a dissertation that’ll provide much-needed dissertation introduction writing help.
Here are some guidelines for you to learn to write a flawless first-class dissertation paper.
Dissertation Introduction Samples & Examples
Check out some basic samples of dissertation introduction chapters to get started.
FAQs about Dissertation Introduction
How to write a dissertation introduction.
- Capture the attention of your reader
- Add the following sections:
- Learn from others
What is the purpose of an introduction chapter?
It’s used to introduce key constructs, ideas, models and/or theories etc. relating to the topic; things that you will be basing the remainder of your dissertation on.
How do you start an introduction in a dissertation?
There is more than one way of starting a dissertation’s introductory chapter. You can begin by stating a problem in your area of interest, review relevant literature, identify the gap, and introduce your topic. Or, you can go the opposite way, too. It’s all entirely up to your discretion. However, be consistent in the format you choose to write in.
How long should a dissertation introduction be?
It can range from 1000 to 2000 words for a master’s dissertation , but for a higher-level dissertation, it mostly ranges from 8,000 to 10,000 words ’ introduction chapter. In the end, though, it depends on the guidelines provided to you by your department.
Dissertation Introduction Checklist
You may also like.
Want to dedicate your dissertation to someone? Learn what a dedication dissertation is, how to write it, and dedication dissertation examples.
Finding it difficult to maintain a good relationship with your supervisor? Here are some tips on ‘How to Deal with an Unhelpful Dissertation Supervisor’.
Dissertation Methodology is the crux of dissertation project. In this article, we will provide tips for you to write an amazing dissertation methodology.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works

Introductions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of introductions, offer strategies for creating effective introductions, and provide some examples of less effective introductions to avoid.
The role of introductions
Introductions and conclusions can be the most difficult parts of papers to write. Usually when you sit down to respond to an assignment, you have at least some sense of what you want to say in the body of your paper. You might have chosen a few examples you want to use or have an idea that will help you answer the main question of your assignment; these sections, therefore, may not be as hard to write. And it’s fine to write them first! But in your final draft, these middle parts of the paper can’t just come out of thin air; they need to be introduced and concluded in a way that makes sense to your reader.
Your introduction and conclusion act as bridges that transport your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis. If your readers pick up your paper about education in the autobiography of Frederick Douglass, for example, they need a transition to help them leave behind the world of Chapel Hill, television, e-mail, and The Daily Tar Heel and to help them temporarily enter the world of nineteenth-century American slavery. By providing an introduction that helps your readers make a transition between their own world and the issues you will be writing about, you give your readers the tools they need to get into your topic and care about what you are saying. Similarly, once you’ve hooked your readers with the introduction and offered evidence to prove your thesis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. (See our handout on conclusions .)
Note that what constitutes a good introduction may vary widely based on the kind of paper you are writing and the academic discipline in which you are writing it. If you are uncertain what kind of introduction is expected, ask your instructor.
Why bother writing a good introduction?
You never get a second chance to make a first impression. The opening paragraph of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions of your argument, your writing style, and the overall quality of your work. A vague, disorganized, error-filled, off-the-wall, or boring introduction will probably create a negative impression. On the other hand, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will start your readers off thinking highly of you, your analytical skills, your writing, and your paper.
Your introduction is an important road map for the rest of your paper. Your introduction conveys a lot of information to your readers. You can let them know what your topic is, why it is important, and how you plan to proceed with your discussion. In many academic disciplines, your introduction should contain a thesis that will assert your main argument. Your introduction should also give the reader a sense of the kinds of information you will use to make that argument and the general organization of the paragraphs and pages that will follow. After reading your introduction, your readers should not have any major surprises in store when they read the main body of your paper.
Ideally, your introduction will make your readers want to read your paper. The introduction should capture your readers’ interest, making them want to read the rest of your paper. Opening with a compelling story, an interesting question, or a vivid example can get your readers to see why your topic matters and serve as an invitation for them to join you for an engaging intellectual conversation (remember, though, that these strategies may not be suitable for all papers and disciplines).
Strategies for writing an effective introduction
Start by thinking about the question (or questions) you are trying to answer. Your entire essay will be a response to this question, and your introduction is the first step toward that end. Your direct answer to the assigned question will be your thesis, and your thesis will likely be included in your introduction, so it is a good idea to use the question as a jumping off point. Imagine that you are assigned the following question:
Drawing on the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , discuss the relationship between education and slavery in 19th-century America. Consider the following: How did white control of education reinforce slavery? How did Douglass and other enslaved African Americans view education while they endured slavery? And what role did education play in the acquisition of freedom? Most importantly, consider the degree to which education was or was not a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
You will probably refer back to your assignment extensively as you prepare your complete essay, and the prompt itself can also give you some clues about how to approach the introduction. Notice that it starts with a broad statement and then narrows to focus on specific questions from the book. One strategy might be to use a similar model in your own introduction—start off with a big picture sentence or two and then focus in on the details of your argument about Douglass. Of course, a different approach could also be very successful, but looking at the way the professor set up the question can sometimes give you some ideas for how you might answer it. (See our handout on understanding assignments for additional information on the hidden clues in assignments.)
Decide how general or broad your opening should be. Keep in mind that even a “big picture” opening needs to be clearly related to your topic; an opening sentence that said “Human beings, more than any other creatures on earth, are capable of learning” would be too broad for our sample assignment about slavery and education. If you have ever used Google Maps or similar programs, that experience can provide a helpful way of thinking about how broad your opening should be. Imagine that you’re researching Chapel Hill. If what you want to find out is whether Chapel Hill is at roughly the same latitude as Rome, it might make sense to hit that little “minus” sign on the online map until it has zoomed all the way out and you can see the whole globe. If you’re trying to figure out how to get from Chapel Hill to Wrightsville Beach, it might make more sense to zoom in to the level where you can see most of North Carolina (but not the rest of the world, or even the rest of the United States). And if you are looking for the intersection of Ridge Road and Manning Drive so that you can find the Writing Center’s main office, you may need to zoom all the way in. The question you are asking determines how “broad” your view should be. In the sample assignment above, the questions are probably at the “state” or “city” level of generality. When writing, you need to place your ideas in context—but that context doesn’t generally have to be as big as the whole galaxy!
Try writing your introduction last. You may think that you have to write your introduction first, but that isn’t necessarily true, and it isn’t always the most effective way to craft a good introduction. You may find that you don’t know precisely what you are going to argue at the beginning of the writing process. It is perfectly fine to start out thinking that you want to argue a particular point but wind up arguing something slightly or even dramatically different by the time you’ve written most of the paper. The writing process can be an important way to organize your ideas, think through complicated issues, refine your thoughts, and develop a sophisticated argument. However, an introduction written at the beginning of that discovery process will not necessarily reflect what you wind up with at the end. You will need to revise your paper to make sure that the introduction, all of the evidence, and the conclusion reflect the argument you intend. Sometimes it’s easiest to just write up all of your evidence first and then write the introduction last—that way you can be sure that the introduction will match the body of the paper.
Don’t be afraid to write a tentative introduction first and then change it later. Some people find that they need to write some kind of introduction in order to get the writing process started. That’s fine, but if you are one of those people, be sure to return to your initial introduction later and rewrite if necessary.
Open with something that will draw readers in. Consider these options (remembering that they may not be suitable for all kinds of papers):
- an intriguing example —for example, Douglass writes about a mistress who initially teaches him but then ceases her instruction as she learns more about slavery.
- a provocative quotation that is closely related to your argument —for example, Douglass writes that “education and slavery were incompatible with each other.” (Quotes from famous people, inspirational quotes, etc. may not work well for an academic paper; in this example, the quote is from the author himself.)
- a puzzling scenario —for example, Frederick Douglass says of slaves that “[N]othing has been left undone to cripple their intellects, darken their minds, debase their moral nature, obliterate all traces of their relationship to mankind; and yet how wonderfully they have sustained the mighty load of a most frightful bondage, under which they have been groaning for centuries!” Douglass clearly asserts that slave owners went to great lengths to destroy the mental capacities of slaves, yet his own life story proves that these efforts could be unsuccessful.
- a vivid and perhaps unexpected anecdote —for example, “Learning about slavery in the American history course at Frederick Douglass High School, students studied the work slaves did, the impact of slavery on their families, and the rules that governed their lives. We didn’t discuss education, however, until one student, Mary, raised her hand and asked, ‘But when did they go to school?’ That modern high school students could not conceive of an American childhood devoid of formal education speaks volumes about the centrality of education to American youth today and also suggests the significance of the deprivation of education in past generations.”
- a thought-provoking question —for example, given all of the freedoms that were denied enslaved individuals in the American South, why does Frederick Douglass focus his attentions so squarely on education and literacy?
Pay special attention to your first sentence. Start off on the right foot with your readers by making sure that the first sentence actually says something useful and that it does so in an interesting and polished way.
How to evaluate your introduction draft
Ask a friend to read your introduction and then tell you what they expect the paper will discuss, what kinds of evidence the paper will use, and what the tone of the paper will be. If your friend is able to predict the rest of your paper accurately, you probably have a good introduction.
Five kinds of less effective introductions
1. The placeholder introduction. When you don’t have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don’t really say much. They exist just to take up the “introduction space” in your paper. If you had something more effective to say, you would probably say it, but in the meantime this paragraph is just a place holder.
Example: Slavery was one of the greatest tragedies in American history. There were many different aspects of slavery. Each created different kinds of problems for enslaved people.
2. The restated question introduction. Restating the question can sometimes be an effective strategy, but it can be easy to stop at JUST restating the question instead of offering a more specific, interesting introduction to your paper. The professor or teaching assistant wrote your question and will be reading many essays in response to it—they do not need to read a whole paragraph that simply restates the question.
Example: The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass discusses the relationship between education and slavery in 19th century America, showing how white control of education reinforced slavery and how Douglass and other enslaved African Americans viewed education while they endured. Moreover, the book discusses the role that education played in the acquisition of freedom. Education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
3. The Webster’s Dictionary introduction. This introduction begins by giving the dictionary definition of one or more of the words in the assigned question. Anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and copy down what Webster says. If you want to open with a discussion of an important term, it may be far more interesting for you (and your reader) if you develop your own definition of the term in the specific context of your class and assignment. You may also be able to use a definition from one of the sources you’ve been reading for class. Also recognize that the dictionary is also not a particularly authoritative work—it doesn’t take into account the context of your course and doesn’t offer particularly detailed information. If you feel that you must seek out an authority, try to find one that is very relevant and specific. Perhaps a quotation from a source reading might prove better? Dictionary introductions are also ineffective simply because they are so overused. Instructors may see a great many papers that begin in this way, greatly decreasing the dramatic impact that any one of those papers will have.
Example: Webster’s dictionary defines slavery as “the state of being a slave,” as “the practice of owning slaves,” and as “a condition of hard work and subjection.”
4. The “dawn of man” introduction. This kind of introduction generally makes broad, sweeping statements about the relevance of this topic since the beginning of time, throughout the world, etc. It is usually very general (similar to the placeholder introduction) and fails to connect to the thesis. It may employ cliches—the phrases “the dawn of man” and “throughout human history” are examples, and it’s hard to imagine a time when starting with one of these would work. Instructors often find them extremely annoying.
Example: Since the dawn of man, slavery has been a problem in human history.
5. The book report introduction. This introduction is what you had to do for your elementary school book reports. It gives the name and author of the book you are writing about, tells what the book is about, and offers other basic facts about the book. You might resort to this sort of introduction when you are trying to fill space because it’s a familiar, comfortable format. It is ineffective because it offers details that your reader probably already knows and that are irrelevant to the thesis.
Example: Frederick Douglass wrote his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave , in the 1840s. It was published in 1986 by Penguin Books. In it, he tells the story of his life.
And now for the conclusion…
Writing an effective introduction can be tough. Try playing around with several different options and choose the one that ends up sounding best to you!
Just as your introduction helps readers make the transition to your topic, your conclusion needs to help them return to their daily lives–but with a lasting sense of how what they have just read is useful or meaningful. Check out our handout on conclusions for tips on ending your paper as effectively as you began it!
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . New York: Dover.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Easily understand how to write a PhD thesis introduction
Feb 26, 2019

Have you checked out the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base ? It’s home to hundreds more free resources and guides, written especially for PhD students.
Get the introduction right and the rest of your dissertation will follow.

What is the purpose of a PhD thesis introduction?
1. establish your research territory (by situating your research in a broader context), 2. establish and justify your niche (by describing why your research is needed) , 3. explain the significance of your research (by describing how you conducted the research).
- What your thesis is about
- Why it is important
- How it was conducted
- How it is laid out
The introduction as a whole should outline the significance and relevance of the thesis. The main criteria for a PhD is its role as an original contribution to knowledge, so the introduction is the space in which you very clearly outline that contribution.
How to structure an PhD thesis introduction
A typical PhD thesis introduction follows the following format:
- Introduction to the introduction: a short version (of only a few paragraphs) of the thesis’ aims, research questions, contribution, objectives and findings.
- State the overarching topic and aims of the thesis in more detail Provide a brief review of the literature related to the topic (this will be very brief if you have a separate literature review chapter)
- Define the terms and scope of the topic
- Critically evaluate the current state of the literature on that topic and identify your gap
- Outline why the research is important and the contribution that it makes
- Outline your epistemological and ontological position
- Clearly outline the research questions and problem(s) you seek to address
- State the hypotheses (if you are using any)
- Detail the most important concepts and variables
- Briefly describe your methodology
- Discuss the main findings
- Discuss the layout of the thesis
Much like the abstract, the reader shouldn’t have to wait long before they understand the contribution, what you are doing and how you are doing it. So, you’ll start by presenting your research in a clear, concise way in the opening few paragraphs. These opening paragraphs should briefly summarise the aims, objectives, research questions, main argument and contribution.
The reader shouldn’t have to wait long before they understand the contribution, what you are doing and how you are doing it.
A useful exercise here is to try and write the core elements of an introduction on a Post-it note. Keep trying until they fit. When they do, use that as the basis for these first few paragraphs. This is the same technique you use when filling out the PhD Writing Template .
As you go through the chapter, you will dial down into more and more detail. That means that the next stage, after the first few paragraphs, is to provide some context (steps 2-10 above).
Here you provide all the detail necessary to situate the study and make sense of the opening few paragraphs.
But, there are two things to bear in mind.
You will need to ease into the detail gently. Don’t launch straight from your opening paragraphs into huge amounts of detail. Follow the order of the 13 steps above and you will gradually ease into your discussion.
The danger of presenting too much information too soon is that you will confuse the reader. They will struggle to understand how the information you present is relevant and will struggle to understand how it relates to your thesis aims and objectives.
Simply follow the steps above.
You need to bear in mind that the level of detail you will go into (and therefore the length of the introduction) depends on the structure of your thesis.
If you have a standalone literature review, you will go into less detail about the current state of the literature and the gaps within it.
Similarly, if you have a dedicated theory chapter, you will not need to spend too much time on developing your theory framework.
The same is true for your methods.
The goal in any case is to present enough context to situate and make sense of your research questions but not overburden the reader with information that is superfluous to the goal of situating the research and which you will repeat at a later juncture anyhow.

Your PhD thesis. All on one page.
Use our free PhD structure template to quickly visualise every element of your thesis.
Common problems when writing your introduction
When we proofread PhDs , we see the same mistakes again and again.
Providing too much detail
There is a tendency to provide too much background information in the introduction. As we saw above, quite how much information you present in your thesis will depend on whether you have a standalone literature review or methods chapter. What you want to avoid is any unnecessary repetition.
Sometimes there is necessary repetition though. You need to present just enough information to contextualise your study and to be able to situate your aims, research questions an argument, but not too much that you end up confusing and bombarding the reader. Keep things simple here; it’s fine to overlook some of the more technical detail at this stage. Think of a newspaper article: the first couple of paragraphs provide a brief overview of the story. The detail comes later.
Not providing enough detail
On the flip side, some students don’t provide enough detail. The danger here is that the reader is left asking questions at the end of the introduction. Remember: they should be able to understand what your thesis is about, how it was conducted and why it is important just from reading the introduction. If you present too little detail then they won’t be able to. Read through your own introduction; is it clear what your contribution is and why it is important? If not, you haven’t got enough detail.
Launching into too much detail
Make sure you introduce gently. Don’t suddenly rush into lots of detail. Instead, you should make the aims, questions and contribution clear in the opening lines and then gradually layer on more detail. That way, the reader can keep up. Present too much detail too soon and the reader will become confused. The last place you want confusion is in the introduction; if the reader can’t follow your introduction, they won’t understand the thesis.
Not following a coherent structure so that the reader is left confused
Some students don’t follow a coherent logic when they write their introductions, which means that the reader is left confused.
For example, if you present too much background information and literature review before you outline the aim and purpose of the research, the reader will struggle to follow, because they won’t know why the background information is important.
The same is true if you discuss the methods before your research questions.
What we see often is important information being spread throughout the introduction in such a way that the reader has to hunt for it. Follow our layout guide above so that each piece of vital information is contained in its own mini section. Make your reader’s job as easy as possible.
Using too much technical language not properly defined
It’s more than likely that your research relies upon lots of technical terms, concepts and techniques. If you must talk about any of these in the introduction, be sure to offer clear and concise definitions. A failure to do so means that the reader is left confused.
Conducting a literature review
Unless you are explicitly avoiding a standalone literature review chapter, the introduction is not the place to review the literature. Sure, you will need to situate your study in a body of literature, but the introduction isn’t the place to critically discuss it or justify its inclusion in that literature. It’s enough to say that you will contribute to X body of literature and briefly discuss its core features and shortcomings. The literature review is the place to justify that decision and elaborate upon its features. Read our guide to writing literature reviews and our guide to being critical when you do so.
Finalising your thesis introduction
Once you have finished your thesis, ask yourself the following questions:
- Does the first line of the introduction discuss the problem that your thesis is addressing and the contribution that it is making?
- Does the introduction provide an overview of the thesis and end with a brief discussion on the content of each chapter?
- Does the introduction make a case for the research?
- Have the research questions/problems/hypotheses been clearly outlined (preferably early on)?
Now you know how to present your research as clearly and concisely as possible. Your reader (and examiner) will thank you, because they’ll be able to understand exactly what your study is about just from reading the introductory pages. Keep this guide to hand, whatever stage of the writing process you are at.
Have you downloaded our free one page PhD Writing Template ? It’s a really effective way to visualise your entire thesis on one page.
If you’re still struggling to structure your introduction, or you need any other support as you write your thesis, check out our one-on-one PhD coaching . It’s like having a personal trainer, but for your PhD.

Share this:
16 comments.
I was struggling with writing the introduction chapter. Really had no idea on how to organise my ideas. Completely lost and desolate. I have no one to encourage or support me. I prayed to God to give me knowledge and wisdom and guide me. After a while I found this site. Praise the Lord. I can’t thank u enough for addressing exactly what’s in my mind. Thank you. Glory be to God for directing me to this site.
All we aim to do here is to make life a little bit easier for PhD students. I know how hard I found it when I was completing mine, so I want to give something back to the community. I’m so pleased you found it useful. Good luck with writing up. If you need any support or if you have any questions at all, email me: [email protected]
Thank you very very much for your information it is resourceful. I was having a problem how to start my introduction.
It’s great to hear you found it useful. Thanks!
Thank you very much for good information to thesis writing
It’s my pleasure!
Hey, this is so useful thankyou! I’m wondering does this apply broadly to all PhD’s including humanities?
Yep – it sure does.
I found this piece of information helpful. I am preparing for my proposal defense in two weeks and needed to refine my introduction. Thank you very much. God bless you richly. I wish we can have a skype conversation.
Thank you again.
thank you, learned from this
Your advice and guidance has become my constant companion in what has been a very stressful time. You write with empathy and understanding. What a wonderful job you are doing for those of us who are too proud to seek advice and support from supervisors or colleagues. Sincerest thanks for taking the loneliness out of writing.
Such nice words. Thank you so much.
this is really useful!!!
Thanks Nora! I’m glad you found it useful.
This is useful and timely. Thank you, please can I email you?
Sure – you can reach out to me at support[at]thephdproofreaders.com
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Join Our Next Four Week Writing Sprint
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023. The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation, appearing right after the table of contents.Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant ...
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write a powerful thesis introduction.
Most thesis introductions include some (but not all) of the stages listed below. There are variations between different schools and between different thesis, depending on the purpose of the thesis. You may also see essay writings. Stages in a thesis introduction. State the general topic and give some background.
A good thesis introduction doesn't shy away from limitations. Instead, it captures the reader's attention by laying them out systematically, often in a dedicated paragraph for each chapter. This honesty allows the reader to understand the research's focus and scope while providing a clear and easy-to-follow structure of the thesis.
An example of a thesis statement in an introduction could be: "This thesis examines how social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and X (formerly Twitter) have reshaped how individuals interact and form relationships in the digital age, with an emphasis on interpersonal communication."Clearly state the main focus and purpose of your research and provide a roadmap for the reader to ...
The length of the introduction will depend on the length of the whole thesis. Usually, an introduction makes up roughly 10 per cent of the total word count. 🍌 How do I write an interesting thesis introduction? The best way to start your introduction is with a sentence that is broad and interesting and that seamlessly transitions into your ...
#1 - The Opening Section. The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you'll be covering in the chapter.. This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and ...
Topic Discussion versus Topic Introduction. Discussing and introducing a topic are two highly different aspects of dissertation introduction writing. You might find it easy to discuss a topic, but introducing it is much trickier. The introduction is the first thing a reader reads; thus, it must be to the point, informative, engaging, and enjoyable.
In many academic disciplines, your introduction should contain a thesis that will assert your main argument. Your introduction should also give the reader a sense of the kinds of information you will use to make that argument and the general organization of the paragraphs and pages that will follow. After reading your introduction, your readers ...
The introduction is the place to factually recount what it is you will be discussing in the thesis. It's something that most students think is simple, but can actually present significant problems.In the one-on-one PhD coaching sessions we run, we see over and over again the problems that writing introductions can pose for PhD students.